As the head of the Main Operational Directorate of the General Staff of the Russian Armed Forces, Colonel-general A.V. Kartopolov remarked on April 15, 2015, “if in the past war was 80 percent combat operations, and propaganda was 20 percent, then in wars today 90 percent of activities consist of information warfare.”
Russia’s information warfare is sustained and unceasing, and, therefore, so should be our defenses.
In George Orwell’s 1984 there are three super-states, Oceania (North and South America, UK, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa), Eurasia (The Soviet Union and Europe), and Eastasia (China, Japan, Korea, northern India). While the boundaries of the superstates have not come to pass quite as Orwell imagined, one could easily see similarities in the power centers of 2021, with China atop Eastasia, Russia atop Eurasia (without Western Europe, of course, although that is becoming a bit squishy), and the USA atop Oceania. One of the elements of Orwell’s if-this-goes-on imagined dystopia was a state of perpetual war.

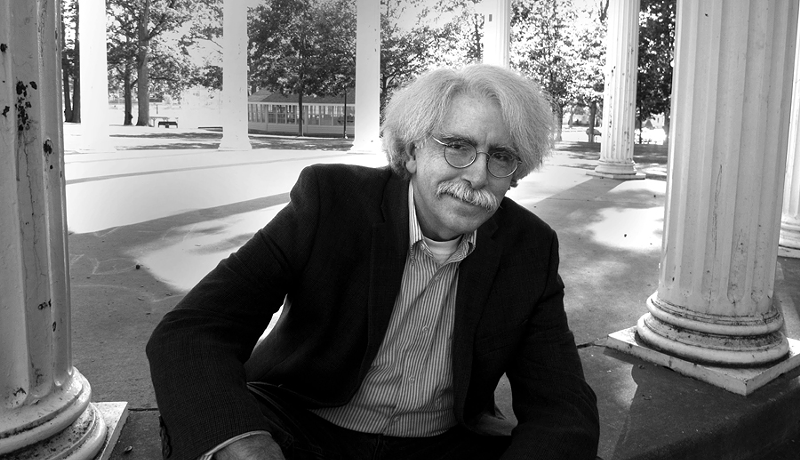
Bilyana Lily – image from Warsaw Security Forum
There is plenty of incentive for those in charge of societies to sustain a war-based economy, whether or not actual wars are fought. War has always been pretty lucrative for some business interests, and offers cover for those in power to attack dissenters as unpatriotic. It has been the case for as long as there have been nations that countries will spy on and seek to manipulate other countries for their own benefit and/or protection. The tools for doing this are diverse, including spying, diplomacy, seeking to impact elections, and the more kinetic special ops, targeted assassinations, and actual tanks-and-planes attacks. But the range of available tools has grown considerably in the last generation. The means for gaining insight into,and of manipulating, the leaders and populations of other countries have become widely available. One result of this is the realization of one of Orwell’s dark visions, albeit in a different form. Russia, under Vladimir Putin, has been engaged in a ceaseless war on other nations for a long time. This warfare does not always entail the use of heavy machinery. It was not tanks that impacted the 2016 presidential election in the USA. It was new, diabolical, and effective weapons of mass communication. The internet, with its social media platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and countless lesser applications, has made everyone accessible, and vulnerable.
Moscow’s attempts to sow popular distrust in governance would not stop after the elections, which are only one event, but would continue after the elections when Russia may attempt to exploit socially divisive themes that could increase suspicion in democratic institutions. And drive communities further apart.
Dr. Bilyana Lily has been looking at this for some time. Born in Bulgaria, she has seen Russian actions from a perspective shared by few general readers. She earned a Masters degree from Geneva Graduate School, in International Relations and Affairs, got another MA at Oxford University, specializing in Russian, Central European, East European and Eurasian Studies, and her PhD from Pardee RAND Graduate School. She has worked at the Bulgarian mission to the United Nations, led DoD research efforts out of RAND, designing analytical tools to predict cyber incidents, and worked on RAND’s election cybersecurity project. Oh, yeah, and she’s a paramedic. Probably has an invisible plane tucked away somewhere, too.
She defines her terms. Just what is considered Information Warfare? How does it fit within Russia’s military planning program? What are each of the actions intended to accomplish? What are the tools the Russians use? Lily selected seven attacks that met her criteria. She limited her study to publicly available information. So, no state secrets are in any danger of being revealed here. She took out of play some attacks that any reasonable person would deem to be at least partly Russia-based, but which lacked publicly accessible confirmations. She looks at what prompts Russia to act and considers differences in how it goes about its operations.
Several chapters of the book are about process. Here is what I am doing. Here are the things I am looking at and the things I am ignoring. Part of this is to talk about a tool she has developed for presenting the gathered information in a graphical format. It could come in handy if you need to update your boss, who is averse to reading. I know, hard to imagine. It may be of considerable use to Intelligence Community (IC) workers, but really, for the rest of us, that element of the book is skippable. It makes for slow, tough reading.
Chapter 1, however, on how Russia sees the world, and thus justifies their actions, is fascinating. It explains a lot. Russian leaders tend to the paranoid and are blind to their own crimes, and the legitimate security concerns of other nations. They see, for example, the bombing of Yugoslavia, the Afghanistan invasion by NATO, the Iraq wars and the operations in Libya as all illegitimate US led attempts at regime change. But Libya was not US-led. If anything, the USA was dragged into that. Afghanistan was the result of 9/11. The first Gulf war came about after Iraq invaded its neighbors, and the West got involved in the former Yugoslavia to prevent Serbian genocide of its neighbors. I guess everything the West does is bad and everything Russia does is ok. They do feel outgunned by the West, though, so feel justified in utilizing asymmetric tactics against their perceived enemies.
Lily uses seven case studies of Russian info warfare. Therein lies the strength of this book. Bet you recognize in the actions taken against other nations many of the actions taken by Russia against the USA. And it will make you very suspicious about the behavior of many on the far right as to exactly what relationships they have with Putin’s Russia. Who is “Q” for example? Personally, I would bet that Q is either a Russian him or herself, was paid for by Russia, or at the bare minimum, was trained and/or advised by Russia. Moscow seeks to foment discord in states it wants to impact. This does not cease when agreements are arrived at over this or that. It does not cease when guns are put down in a conflict here or there. Warfare for Russia is a permanent state. They are always trying to pit group against group, whether in the USA, France, Germany, or any other nation which has interests that clash with Russia’s.
…this book analyzes under what conditions, in what contexts, and in what combinations with other nonmilitary and military measures Russia has employed certain types of cyber operations. In particular, this book explores what conditions have been associated with the employment of various types of Russian state-sponsored cyber operations against political IT infrastructure of NATO countries and invited members.
Lily arrives at some conclusions about what the parameters are that define what Russia will do, and how far it will go. For some countries, this and then that. For other countries, only this. And it looks at what Russia hopes to accomplish with various actions. In some cases, there is hardcore spying involved, assassinations, bombings, concerted attempts to disrupt electoral systems, for example. But in others, Russia acts merely to undermine people’s confidence in electoral systems, or the viability of target governments.
If we had paid more attention to Russian military doctrine, we could have been better prepared for what happened in 2016. [in Russia’s attack on the USA election] – from the JSOU presentation
Gripes – When I was in graduate school, a professor once said that the standard format for reports to be submitted, not only in his class, but in the jobs we were training for, was 1) Say what it is you are going to say 2) Say it, and then 3) Say what it is you have just said. Lily follows this formula not only for the overall book, but within each chapter. It makes life particularly easy for those looking to speed read their way through this, but for those of us who insist on reading every word, that element was a bit of a chore. It reads as a very academic paper. No problem for folks in the field, but off-putting to the more casual reader. While it is understandable that Lilly restricts her case studies to those with publicly provable Russian connections, I was yearning for her to go a bit beyond, and incorporate looks at instances in which it is plain what is going on, despite there not being public proof beyond a reasonable doubt.
Not gripes – Clearly explaining Russia’s motivation and world view. Read these case studies and you will recognize much that is going on all around us, get a sense of how Russia goes about manipulating populations. Breaking down the methods, aims, and impacts lets one talk about information warfare in specific, rather than general terms, and thereby consider actions that target individual elements for ways to defend.
It is often the case that analytical books that delve into political or social problems offer excellent insight, but fall short when it comes to offering real-world solutions. One can look at successes that targeted nations have had in beating back or preventing Russian Info attacks, and seek to apply those best practices across the board, for NATO nations in particular. Thankfully, some of Lilly’s advice seems doable.
She recommends that states should make public more of the information on cyber operations and actors directed against them, to help understand Russia’s playbook. There are benefits to be had beyond that as we saw recently, when President Biden publicly outed Russia’s plan to fake attacks on Russians and blame Ukraine, as a justification for their invasion. She also recommends transparency in political party funding sources. This really is a no-brainer, but the reality is that it is currently, and for the foreseeable future will remain, a non-starter federally in the USA where so many of those in charge of making the laws benefit directly from that very secrecy. She also recommends federal funding of cyber-awareness training for state and local campaigns. I can certainly see this meeting resistance from those legislators who might benefit from external interference in our elections. It might have a chance in individual states as a state program. There are more. It is a mixed bag, containing no silver bullet. The inherent conflicts of interest will keep the USA vulnerable. At this point we have to rely on the IC and the Department of Defense to fend off the gravest attacks. Clearly, relying on the moral concerns of companies like Facebook and Twitter (now owned by dodgy-human Elon Musk) is a sure cure for any feeling of security.
Lilly may not have all the solutions, but she has gone a very long way in identifying the problems, at least as far as Russia goes, pointing out what is likely, and under what circumstances, and letting us know where such attacks have failed and why. In the larger sense, she has made it very clear that Russian military policy contains a drive to ongoing information warfare. If you want to understand how Russia seeks to undermine Western democracies, see the techniques they use, and understand their fondness for using local allies, or puppets, Russian Information Warfare is a must read.
For Russia a particularly useful way to keep the West, or Russia’s enemies in general at bay, is to wage an information-based assault on them all, constantly. Why take casualties when you can achieve your objectives by conducting daily operations on the sly. Orwell would recognize the notion. For Russia, permanent War is Peace.
Information warfare is applied through strategic media messaging disseminated through all media channels that reach the population of the targeted country. The aggressive party uses information technologies to engage public institutions in the targeted country, such as mass media, religions institutions, NGOs, cultural institutions, and public movements receiving foreign financing. To further help the demoralization of the population and ensure chaos, the adversary targets the disillusioned population and infiltrates these groups with provocateurs. Disinformation, or deliberate falsification of events, can also be considered among the principal information warfare components.
Review posted – April 15, 2022
Publication date – September 15, 2022
I received an EPUB ARE of Russian Information Warfare from The U.S. Naval Institute in return for a fair review and agreeing not to give away any state secrets. Thanks, folks. And thanks to NetGalley for facilitating.




This review has been cross-posted on GoodReads
An aside: I received a NetGalley EPUB ARE of this book in March, 2022. As noted above it is not due for publication until September, 2022. In the normal course of events, I would have waited to read and review it until much nearer the pub date. But given Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, it seemed important to push this one to the head of the line. It may not yet be available for sale, but if you are interested, I suggest checking NetGalley for a possible early look.
=======================================EXTRA STUFF
Lilly’s FB and Twitter pages
From the U.S. Naval Institute:
Denounced by the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Dr. Bilyana Lilly managed projects on ransomware, cyber threat intelligence, AI, disinformation, and information warfare. She was a cyber expert for the RAND Corporation and has spoken at DefCon, CyCon, the Executive Women’s Forum and the Warsaw Security Forum. Dr. Lilly is the author of over a dozen peer-reviewed publications and has been cited in the Wall Street Journal, Foreign Policy and ZDNet.
Interview
—–The Office of Strategic Engagement – Think JSOU – Interview with Dr. Bilyana Lilly by Lieutenant Colonel Mitch Wander – this is really more of a staged Q/A to enable Lilly to talk about her material. It is very informative, but with a particularly stiff question-reading by Wander. – This is the only one you will need.
Item of Interest from the author
—–International Committee of the Red Cross – Intercross – THE RISE AND FALL OF THE ABM TREATY: MISSILE DEFENSE AND THE U.S.-RUSSIA RELATIONSHIP – 1:20:42 – Lilly is a panel member discussing James Cameron’s book The Double Game
Items of Interest
—–NY times – 3/4/2022 – I’ve Dealt With Foreign Cyberattacks. America Isn’t Ready for What’s Coming. By Glenn S. Gerstell
—–NY Times – 11/12/2018 – Operation InfeKtion – Russian disinformation: From Cold War to Kanye by Adam B. Ellick and Adam Westbrook – a three-part video series
—–The Guardian – 3/5/20922 – Ukrainians around the world aren’t just protesting –we’re fighting an information war by Jane Lytvynenko
—–Lockheed Martin – Cyber Kill Chain
—–National Technical Reports Library – 2017 – Defense Science Board (DSB) Task Force on Cyber Deterrence -you can download the report
Although progress is being made to reduce the pervasive cyber vulnerabilities of U.S. critical infrastructure, the unfortunate reality is that, for at least the next decade, the offensive cyber capabilities of our most capable adversaries are likely to far exceed the United States’ ability to defend key critical infrastructures. The U.S. military itself has a deep and extensive dependence on information technology as well, creating a massive attack surface.
…due to our extreme dependencies on vulnerable information systems, the United States today lives in a virtual “glass house.” Hardening and increasing the resilience of the most vital critical infrastructure systems – including electricity, water, and waste water – is urgently needed to bolster deterrence by denial and by cost imposition.
—–NY Times – 3/18/22 – Why You Haven’t Heard About the Secret Cyberwar in Ukraine by Thomas Rid
—–AP – April 2, 2022 – Ukraine says potent Russian hack against power grid thwarted by Frank Bajak
—–NY Times – April 13, 2022 – U.S. and Ukrainian Groups Pierce Putin’s Propaganda Bubble By Julian E. Barnes and Edward Wong
During the Cold War, the U.S. government, and the C.I.A. specifically, helped found and fund independent media organizations with the mission to penetrate the Iron Curtain with fact-based news. With the invasion of Ukraine, the organizations are once again operating with a sense of urgency as they push to get accurate information inside an authoritarian state.
—–NY Times – April 15, 2022 – How Russia Media Uses Fox News to Make Its Case by Stuart A. Thompson
—–AP – April 28, 2022 – A chilling Russian cyber aim in Ukraine: Digital dossiers by Frank Bajak
—–NY Times – May 6, 2022 – The War in Ukraine, as Seen on Russian TV by Stuart A. Thompson
——AP – July 15, 2022 – Russia’s information war expands through Eastern Europe By David Klepper
—–Red Pen of Doom – September 14, 2022 – Top 7 ways Ukraine beat Russia on the information battlefield by Guy Bergstrom